FOOD
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
Mary Earle, Richard Earle and Allan Anderson |
| Loading
|
for success |
|
||||
|
|
|
Part
I,
Chapter 1
Keys to new product success and failure 1.4 Product development process: the basis for success The PD Process is important in the food industry,
as in all other industries. There is a need for a multidiscipline, multifunctional,
well-defined process frame on which the company's different projects
can be planned (Rosenau, 1996). In an American survey (Griffin,
1997), 60% of the firms surveyed used formal stages with inter- stage
reviews and recycling such as the Stage-GateTM process (Cooper 1990,
1996b), but most companies had developed relatively flexible gates and
stage structures. Earle and Earle (1999) suggested a simpler version of four stages - product strategy development, product design and process development, product commercialisation and product launching and evaluation which more clearly delineated the skill and knowledge areas required as shown in Fig. 1.5. 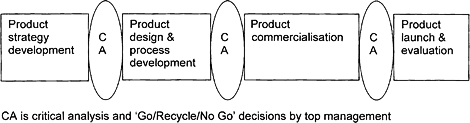 Fig. 1.5 The fundamental PD Process. Decisions between the stages are identified and then the necessary knowledge outcomes from the stages for these decisions are identified. Then the activities within the stages are identified and finally the techniques for these activities chosen. This gives a clear basis for planning the project: Decisions which will give the sequence leading to the critical analysis and decision making: Results In other words, at the start decide on where the project is going, identify the resources available in people, equipment, time and money, then decide how to get to the successful outcome and have an efficient PD Process. |
|
 |